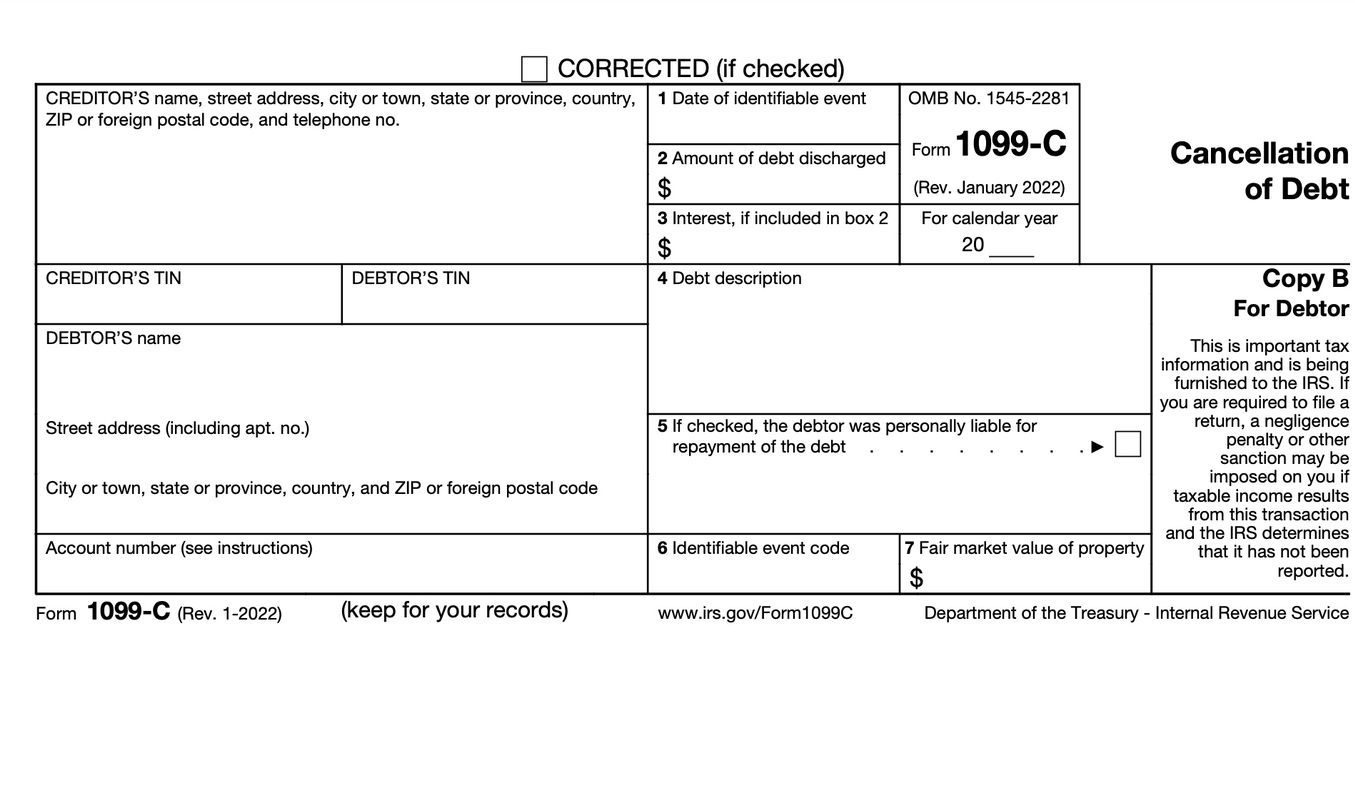
What Is IRS Form 1099C?
If a taxpayer has a debt that has been forgiven or canceled by the lender for less than what they owed, they should receive IRS Form 1099C from the lender. However, the amount canceled or forgiven must be at least $600 before a lender is mandated to send the taxpayer and the IRS a 1099C.
A 1099C asks several questions about a forgiven or canceled debt. The IRS wants to know the exact date the debt was discharged, the amount of debt discharged, what type of debt was discharged, and the fair market value of any properties involved with the discharge.
Who Sends You a 1099C When Your Debt is Canceled, Discharged, or Forgiven?
The entity (lender) canceling, forgiving, or otherwise discharging the debt is responsible for sending a 1099C to the individual being relieved of the debt. The lender must also send a completed 1099C to the IRS when the amount canceled or forgiven is $600 or more.
Here are examples of when a lender cancels a debt and must send or does not have to send a 1099C to the IRS or taxpayer:
After losing his job, John could not pay his mortgage. He still owed $120,000 on his mortgage. The mortgage lender foreclosed on his house and held an auction to sell the house. Someone bought the house at the auction for $115,000. The mortgage company then canceled the $5,000 that John still owed on his mortgage. Since this amount exceeds $600, the mortgage company must send a 1099C to the IRS and John.
Alternatively, if John’s mortgage company had sold the house for $119,700, neither the mortgage company nor John would need to submit a 1099C to the IRS because the amount forgiven is less than $600.
What Types of Debt Cancellation/Forgiveness Are Reported on 1099C Tax Form?
The IRS states that “in general, if you owe a debt to someone else, and they forgive or cancel that debt for less than its full amount, you may be considered as having taxable income”.
In other words, the scenario with John still owing $5,000 to his mortgage company after his house was sold at auction, followed by the mortgage company canceling the entire debt, means John may have to pay taxes on that $5,000 forgiven.
Other types of debt cancellation or forgiveness often involving IRS Form 1099C include:
- Abandonment of a property
- Repossession of a vehicle or other valuable item for nonpayment
- Returning property to a lender
- Modification of loan(s) on a primary residence
- Settling a credit card debt
Does the IRS Consider Canceled Debt as Income?
If you owe $10,000 on a credit card and the credit card company agrees to cancel the entire debt if you pay $5,000 on the debt, the $5,000 you did not have to pay must be reported to the IRS as possible taxable income. When the amount reported on 1099C is more than $600, that amount is typically taxed according to the tax bracket in which you fall.
If you owe $10,000 on a credit card, pay off $9,500 of that debt, and the credit card company agrees to cancel the remaining debt of $500, you do not have to report the $500 forgiveness to the IRS.
How Do You Report 1099C Form on Your Tax Return?
If your canceled or forgiven debt is more than $600 and you have to include it on your tax return, you’ll report your 1099C amount as “other” income on 1040 Schedule 1.
Is Canceled Debt Taxable If You File for Bankruptcy? What Other Types of Canceled Debt Aren’t Taxable?
No, canceled debts are not taxable when a judge has granted your request for bankruptcy. Some other types of canceled debts that are not taxable under IRS guidelines include:
- Insolvency
- Forgiven student loans
- Public service loan forgiveness
- Secured (nonrecourse) debts
However, the IRS sometimes expects taxpayers with these types of forgiven debts to report them using form 982. This form determines whether the amount of canceled debt is applicable to a taxpayer’s gross income.
What Happens If You Don’t Report a Canceled Debt Using 1099C?
Any taxes you owe on a canceled, discharged, or forgiven debt will accrue interest just like other tax debts. If the IRS audits your taxes and finds discrepancies involving a canceled debt that should have been reported as taxable income, they will mail a letter requesting you amend your federal tax return and pay any taxes, plus interest and penalties.
If you do not believe you had to report your canceled debt as income on your federal tax return, contact the IRS to dispute your 1099C.
6 Simple Questions. Free Evaluation.
Join our Newsletter
Enter your email address to join our free newsletter. Get all the latest news and updates.